Which of These Describes Loose Connective Tissue
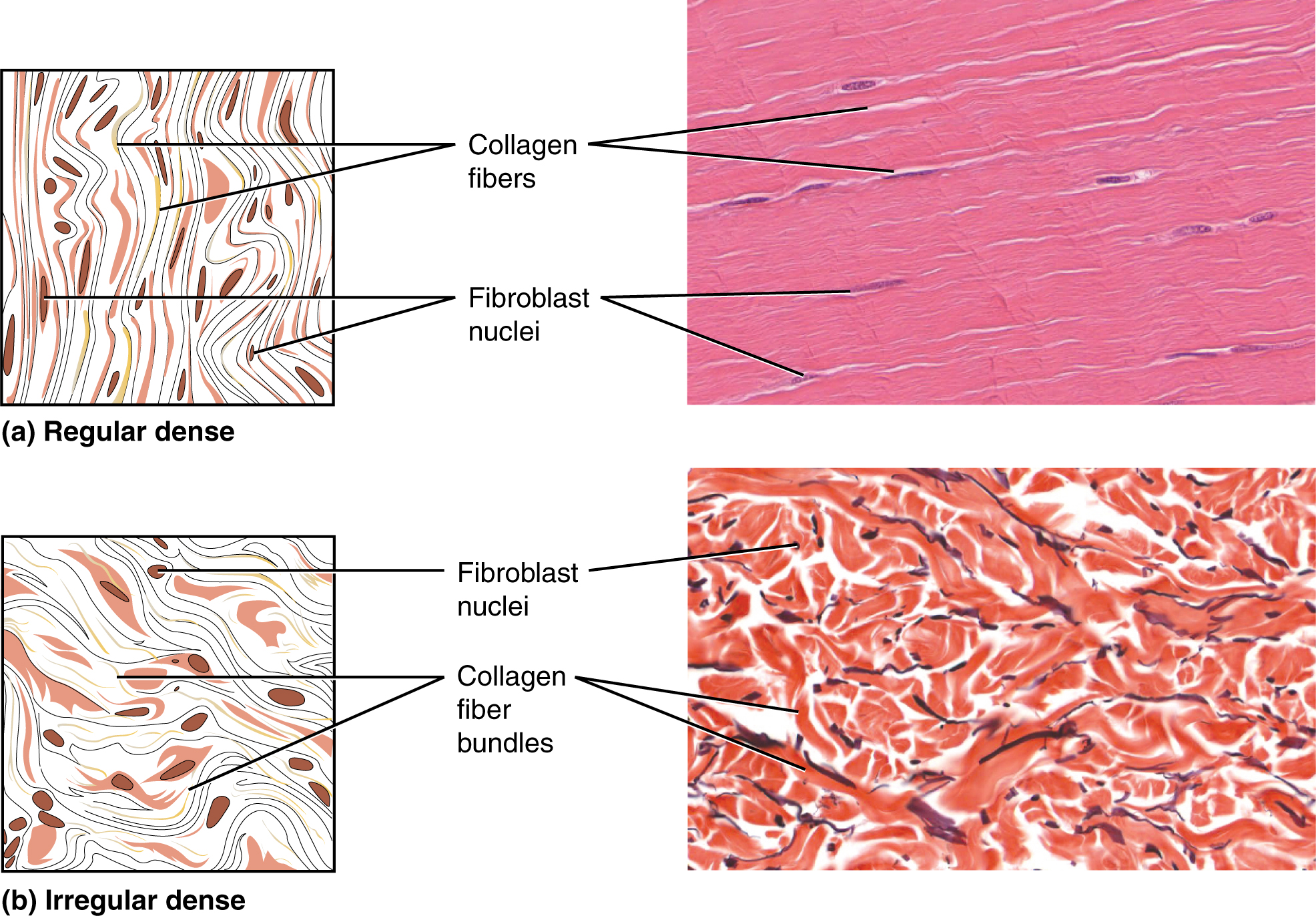
Dense Connective Tissues 3. It occurs in small elongated bundles separated by regions that contain ground substance.

Connective Tissues Loose Loose Connective Tissue Tissue Biology Tissue Types
Loose areolar connective tissue is the most abundant form of collagenous connective tissue.
. Describe the layers of the skin and the functions of each layer. There are three types of loose connective tissue. Connective tissue proper includes.
Connective tissue can be classified as either connective tissue proper or specialized connective tissue. Which of these describes loose connective tissue. Which of these describes loose connective tissue.
It is a loose weave of fibers that functions as a packing material. It contains some cells called plasma cells finer elastin fibres and thicker collagen fibres. Try to identify the cells and fibres.
This is an embryonic type of loose connective tissueit is a spongy tissue that serves as packing between the developing structures of the an embryo. Specialized Connective Tissues Adipose Tissue. How does connective tissue differ from the other three major tissue types.
These are cells that remain in the loose connective tissue at all times. 321A with lymphocytes plasma cells macrophages eosinophils neutrophils and mast cells as well as fibroblasts and occasional fat cells see Chapter 28 for details on these cells. This is an example of loose connective tissue from a lymph gland.
Loose areolar connective tissue and adipose tissue which functions as a mode of fat storage and provides insulation and cushioning for the integument. In addition they nourish and pillows. Areolar loose Connective Tissue.
Types of Connective Tissues. Neutrophils and macrophages are also present and both are discussed below. Loose connective tissues are present all over the body where support and elasticity both are needed.
Areolar adipose and reticular connective tissue. Elastic tissue consists primarily of elastic fibers or fenestrated elastic laminae and is limited in distribution to certain ligaments and the elastic laminae of larger arteries. The fixed cells of the loose connective tissue are fibroblasts macrophages adipocytes or fat cells and mast cells.
These tissues are of. It allows water salts and various nutrients to diffuse through to adjacent or embedded cells and tissues. Which of these describes loose connective tissue.
The lamina propria of the alimentary and respiratory tracts mucous membranes of reproductive and urinary tracts glands mesentery and dermis of the skin. Loose Areolar Connective Tissue. This micrograph shows.
This variety of defensive. Connective tissue often consists of relatively few cells embedded in an extracellular matrix. Loose Connective Tissue large amounts of ground substance and fewer fibers Aerolar.
It transports nutrients and gases from one part of the body to another. Dense Connective Tissue large amounts of fibers and less ground substance Dense Regular. Adipose lines organs and body.
Loose connective tissue also called areolar and dense irregular connective tissue. Dense regular connective tissue cartilage bone adipose tissue blood and hematopoietic tissue. A It is a loose weave of fibers that functions as a packing material.
Categories of connective tissue include the following. Areolar connective tissue is the most abundant form of connective tissue in vertebrate organisms. Loose Connective Tissues 2.
Blood vessels nerves and muscles all have a loose connective tissue wrapping. The loose connective tissue underlying the epithelium in the gastrointestinal tract is a good example of this heterogeneity Fig. Areolar connective tissue is often used synonymously with loose connective tissue.
Examples of loose connective tissue include. This type of tissue contains many cells a loose arrangement of fibres and. They are a loose array of random fibers that has a wide variety of cell type.
Types of Loose Connective Tissue. D It transports nutrients and gases from one part of the body. C It is a rigid material that provides structural support.
This region is also a loose irregular connective tissue but can be so extensively infiltrated by white blood cells and plasma cells that the supporting fibers and ground substance are obscured. Adipose tissue is a loose connective tissue in which fat cells predominate. They form the subcutaneous layer under the skin along with adipose tissues attaching muscles and other structures to the skin.
Loose connective tissue is found between many organs where it acts both to absorb shock and bind tissues together. Dense connective tissue is enriched in collagen fibers with little ground substance. Learn the structure and function of loose connective tissue here.
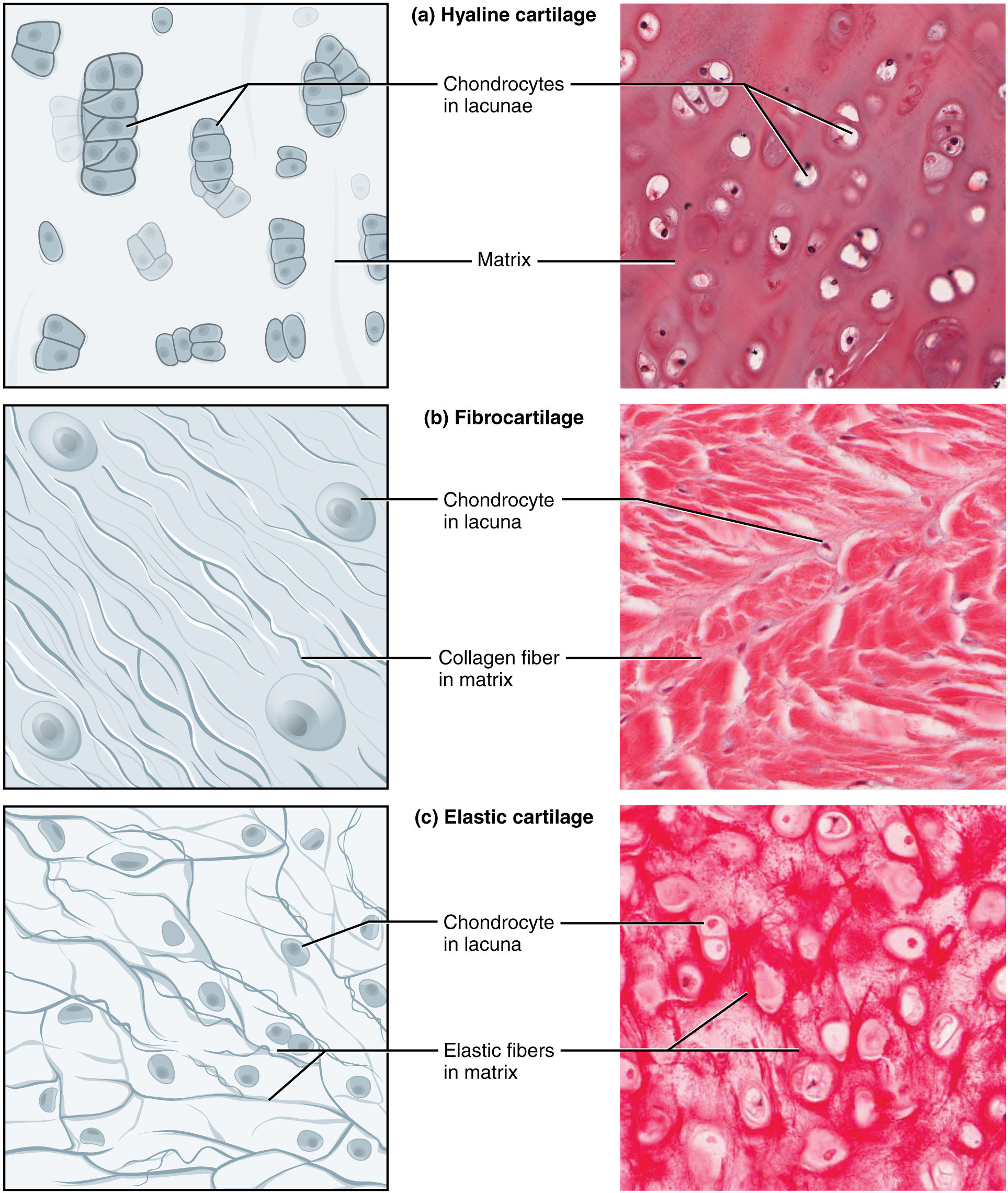
Specialized connective tissue types include. This micrograph shows hyaline cartilage a semi-rigid connective tissue from a human trachea windpipe. It is a loose weave of fibers that functions as a packing material It is composed of many fibers that connect bone to bone and muscle to bone It is a rigid material that provides structural support.
Adipose tissue is a form of loose connective tissue that stores fat. There are seven types of connective tissues found in the body of people. This tissue has cells and fibres loosely arranged in a semifluid ground substance.
3 rows Loose connective tissue LCT also called areolar tissue belongs to the category of. These cells are especially abundant on the surfaces of the hands and feet. B It is composed of many fibers that connect bone to bone and muscle to bone.
Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And Physiology

Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And Physiology
Comments
Post a Comment